Brand Positioning (web2 vs. web3)
Brand positioning strategy differs significantly between Web2 and Web3 due to a shift in core principles from centralization and data ownership by corporations (Web2) to decentralization, user empowerment, and community ownership (Web3).
Web2 Positioning (Centralized) vs. Web3 Positioning (Decentralized)
Core Web3 Positioning Strategies (2026)
Community as the Brand: In Web3, the community is not just an audience but an active stakeholder. Success is defined by the strength of your Discord or Telegram communities and user participation in governance via DAOs.
Radical Transparency: Positioning is built on "provable authenticity". Brands must share tokenomics, open-source their code, and provide on-chain verification of claims to build trust in a decentralized space.
Digital Ownership & Utility: Use NFTs and tokens to provide fractional ownership or exclusive access. This shifts the value proposition from a functional product to a tokenized network where users benefit from the ecosystem's growth.
Decentralized Identity: Position around privacy and user autonomy. Users in 2026 increasingly gravitate toward brands that respect their "self-sovereign identity," allowing them to control their data across platforms.
Hybrid Models (Web2.5): Established brands like Nike are bridging the gap by blending traditional marketing with Web3 elements like virtual wearables and token-gated communities to reach new audiences while maintaining existing brand equity.
Web2 vs. Web3 Positioning Comparison
Web2 Positioning (Centralized) vs Web3 Positioning (Decentralized)
Authority
Web2: Corporate-owned; brand controls narrative.
Web 3: Community-governed; users are stakeholders.
Trust Source
Web2: Brand reputation and third-party validation.
Web3: Transparency, open-source code, and on-chain proof.
Relationship
Web2: Transactional (Customer/User).
Web3: Participatory (Co-creator/Owner).
Engagement
Web2: Funnel-based; focus on clicks and conversions.
Web3: Meme-driven; focus on viral culture and "movements".
Loyalty
Web2:Platform-locked; based on product quality.
Web3: Portable; based on shared values and digital ownership.
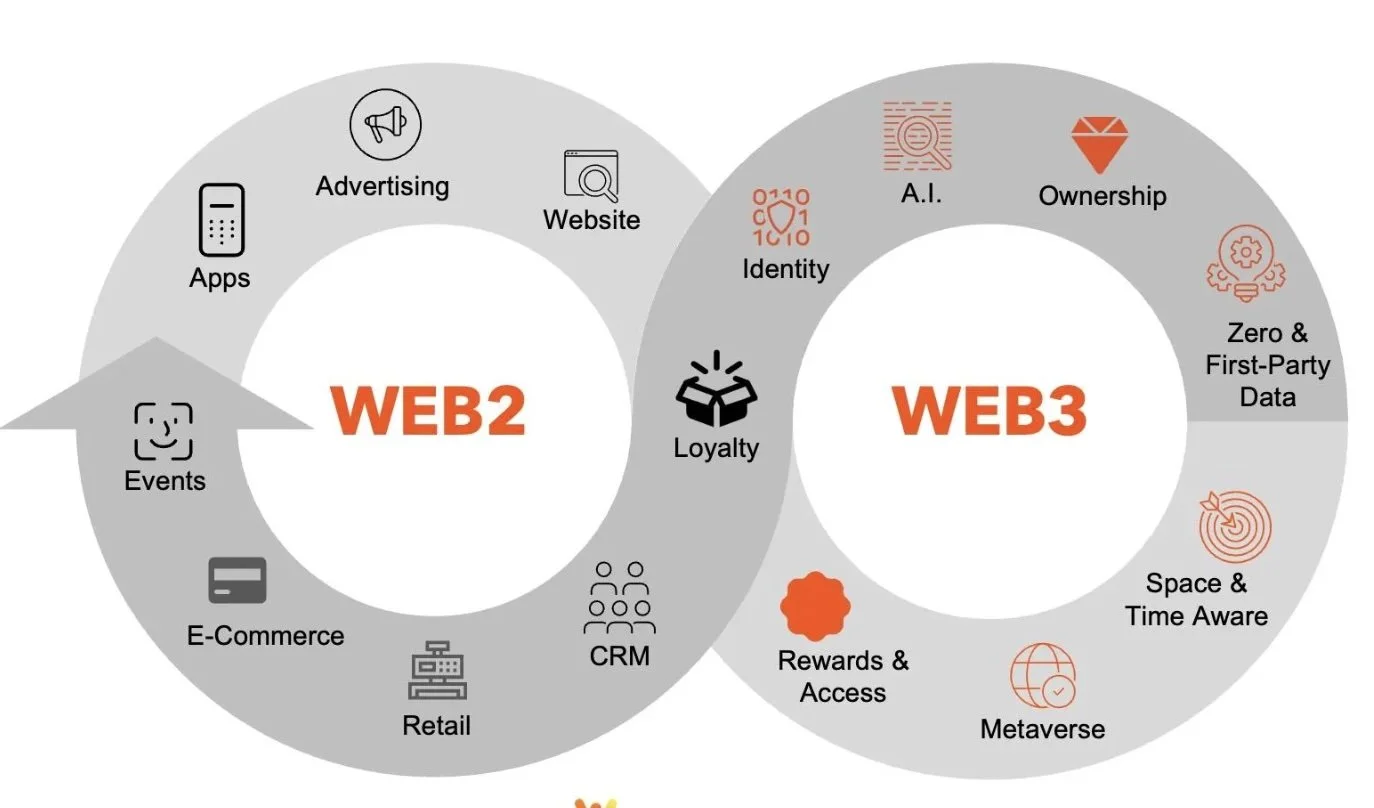
The image is a Venn diagram illustrating the differences and overlaps between Web2 and Web3. It highlights that Web2 is centered around advertising, websites, e-commerce, and apps, while Web3 focuses on A.I., ownership, zero & first-party data, and the metaverse. Loyalty, CRM, Events, and Retail are shown as overlapping areas, representing concepts present in both iterations of the internet.
Key Distinctions
Web2 is characterized by centralization, where user data and content are primarily controlled by large corporations and stored on their servers (e.g., Google, Facebook). Monetization often relies on advertising and selling user data.
Web3, built on blockchain technology, is decentralized, giving users control and ownership over their data and digital assets through cryptographic keys and smart contracts. It emphasizes transparency, security, and user-centricity, allowing for new economic models like NFTs and cryptocurrencies.
Overlapping Concepts
Loyalty programs in Web3 are evolving from simple points systems to tokenized rewards (like NFTs) that users truly own and can trade across different platforms, offering a deeper connection and real value beyond a single brand ecosystem.
Events and Retail are integrating Web3 elements, such as using NFTs for exclusive access to experiences or creating digital wearables for avatars in the metaverse, blending physical and digital interactions.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is adapting to use transparent on-chain data for more personalized and secure customer engagement strategies without relying on traditional centralized databases.
Technologies and applications that enable this transition from Web2 to Web3:
Web3 is powered by a stack of core technologies, primarily built on the foundation of blockchain, designed to shift power and ownership from centralized entities back to the users.
Core Technologies
Blockchain The foundational technology of Web3 is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. This eliminates the need for a central authority and provides transparency and security.
Smart Contracts These are self-executing lines of code that automatically enforce the terms of an agreement when certain conditions are met, all without intermediaries. They are the backbone for dApps and much of the Web3 functionality.
Cryptography and Digital Wallets Web3 relies heavily on cryptographic keys. Users manage their digital assets and identity through non-custodial wallets (e.g., MetaMask), giving them full control and ownership of their data and assets.
Decentralized Storage To manage large amounts of data (like images for NFTs), systems like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) and Filecoin are used. Data is broken into pieces, encrypted, and distributed across a peer-to-peer network, making it censorship-resistant and resilient to failure.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML) These technologies help Web3 applications interpret the context of data (the "semantic web"), enabling more personalized and intelligent user experiences.
Oracles Oracles act as a bridge between the blockchain and real-world, off-chain data sources (like weather or price feeds), allowing smart contracts to react to external events.
Applications and Use Cases (dApps)
Decentralized applications (dApps) are built on these technologies and cover various domains:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms for lending (Aave), borrowing, trading (Uniswap), and earning interest on cryptocurrency without traditional banks.
NFT Marketplaces Platforms like OpenSea allow users to buy, sell, and mint non-fungible tokens, which represent unique ownership of digital assets like art, music, or in-game items.
Gaming (GameFi) Play-to-earn games like Axie Infinity incorporate NFTs as in-game assets, allowing players to truly own and profit from their virtual items.
Metaverse Virtual worlds where users can buy digital land (e.g., The Sandbox) and interact using their Web3 identities and assets.
Social Networks Decentralized social media platforms like Steemit give users more control over their content and data, often rewarding engagement with cryptocurrency.
Supply Chain Management Blockchain is used to provide transparent and tamper-proof tracking of products from production to sale